Exploring Japanese Cultural Wealth Through Map of Japan Accompanied by Legend
3rd Jan 2024
Bab 1: Pengenalan
Pentingnya Memahami Kekayaan Budaya Melalui Peta Keanekaragaman budaya Jepang
Bab pertama dalam outline tersebut, "Pengenalan", bertujuan untuk memberikan pemahaman kepada pembaca tentang pentingnya memahami kekayaan budaya melalui peta dan memberikan gambaran umum tentang keanekaragaman budaya Jepang.
Pentingnya Memahami Kekayaan Budaya Melalui Peta Peta memiliki peran penting dalam memahami kekayaan budaya suatu tempat. Peta tidak hanya sekedar sebagai alat bantu navigasi, namun juga sebagai medium yang dapat memberikan gambaran tentang keanekaragaman budaya suatu wilayah. Melalui peta, kita dapat melihat bagaimana kebudayaan suatu tempat tercermin dalam tata letak geografisnya, simbol-simbol yang digunakan, dan cara wilayah-wilayah tersebut direpresentasikan. Ketika kita memahami peta secara lebih dalam, kita juga dapat memperoleh pemahaman yang lebih mendalam tentang budaya suatu tempat.
Gambaran Umum tentang Keanekaragaman Budaya Jepang Jepang memiliki keanekaragaman budaya yang sangat kaya. Dari utara hingga selatan, Jepang memiliki beragam tradisi, bahasa, makanan, festival, dan sebagainya. Keanekaragaman ini juga tercermin dalam berbagai aspek kehidupan masyarakat Jepang, seperti peta, pertunjukan seni, dan sejarah. Dengan memahami keanekaragaman budaya Jepang, kita dapat lebih menghargai warisan budaya yang dimiliki oleh negara ini.
Dengan paparan ini, pembaca dapat memahami bahwa penggunaan peta tidak hanya sebagai alat navigasi, namun juga sebagai media untuk memahami keanekaragaman budaya suatu tempat. Kemudian, pembaca diperkenalkan dengan keanekaragaman budaya Jepang secara umum, sehingga mereka dapat menangkap kompleksitas dan kekayaan budaya yang dimiliki oleh Jepang.
BAB 2: The Significance of Maps in Japanese Culture
Peta bukan hanya sekadar alat navigasi atau representasi fisik dari suatu wilayah, tetapi juga merupakan cerminan dari budaya, sejarah, dan nilai-nilai masyarakat yang menciptakannya. Dalam budaya Jepang, peta memiliki arti yang sangat penting dan mendalam. Bab ini akan menjelaskan tentang pentingnya peta dalam budaya Jepang serta bagaimana peta menjadi bagian integral dari warisan budaya Jepang.
Sub Bab 2.1: Penggunaan Historis Peta di Jepang
Peta telah digunakan secara luas di Jepang sejak zaman kuno, baik untuk kepentingan administratif dan militer, maupun sebagai representasi spiritual dan mitologis. Selama periode Edo, peta digunakan untuk memetakan wilayah-wilayah feodal dan sistem jalan, yang merupakan contoh dari kecanggihan teknik peta pada masa itu. Selain itu, peta-peta historis juga sering kali menampilkan simbol-simbol dan gambar-gambar yang memiliki makna spiritual dan religius, menunjukkan bagaimana peta dalam budaya Jepang merupakan gabungan antara aspek fisik dan metafisik dari suatu wilayah.
Sub Bab 2.2: Simbolisme dan Representasi dalam Kartografi Jepang
Peta Jepang memiliki simbolisme yang kaya dan unik, yang mencerminkan nilai-nilai budaya dan spiritual dalam masyarakat Jepang. Misalnya, gunung di peta sering kali dianggap sebagai tempat suci atau pemandangan spiritual, sehingga memberikan dimensi simbolis yang lebih dalam dalam representasi geografisnya. Selain itu, penggunaan warna, pola, dan simbol-simbol lainnya juga memiliki makna yang dalam dalam konteks budaya Jepang. Hal ini menunjukkan betapa peta bukan hanya alat representasi spasial, tetapi juga merupakan medium untuk menyampaikan makna dan simbol-simbol yang memperkaya pemahaman tentang sebuah wilayah.
Dengan mengetahui pentingnya peta dalam budaya Jepang serta bagaimana peta-peta tersebut menjadi sarana representasi budaya dan simbolisme yang kaya, kita dapat memahami betapa nilai dan makna dari peta dalam konteks budaya Jepang sangatlah penting. Pemetaan bukan hanya sekadar aktivitas teknis, tetapi juga merupakan warisan budaya yang hidup, yang terus menerus mencerminkan nilai dan simbol-simbol dalam masyarakat Jepang.
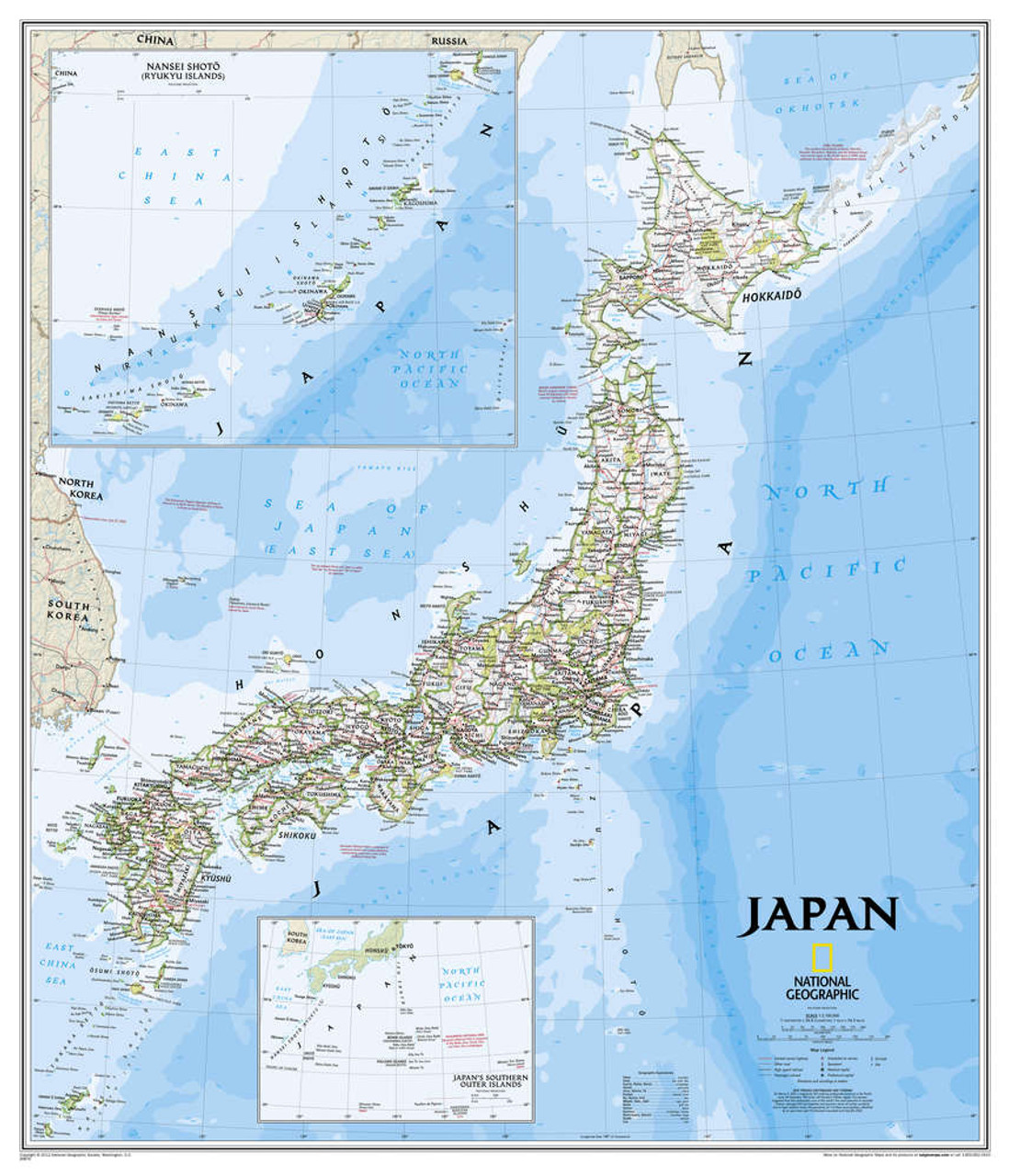
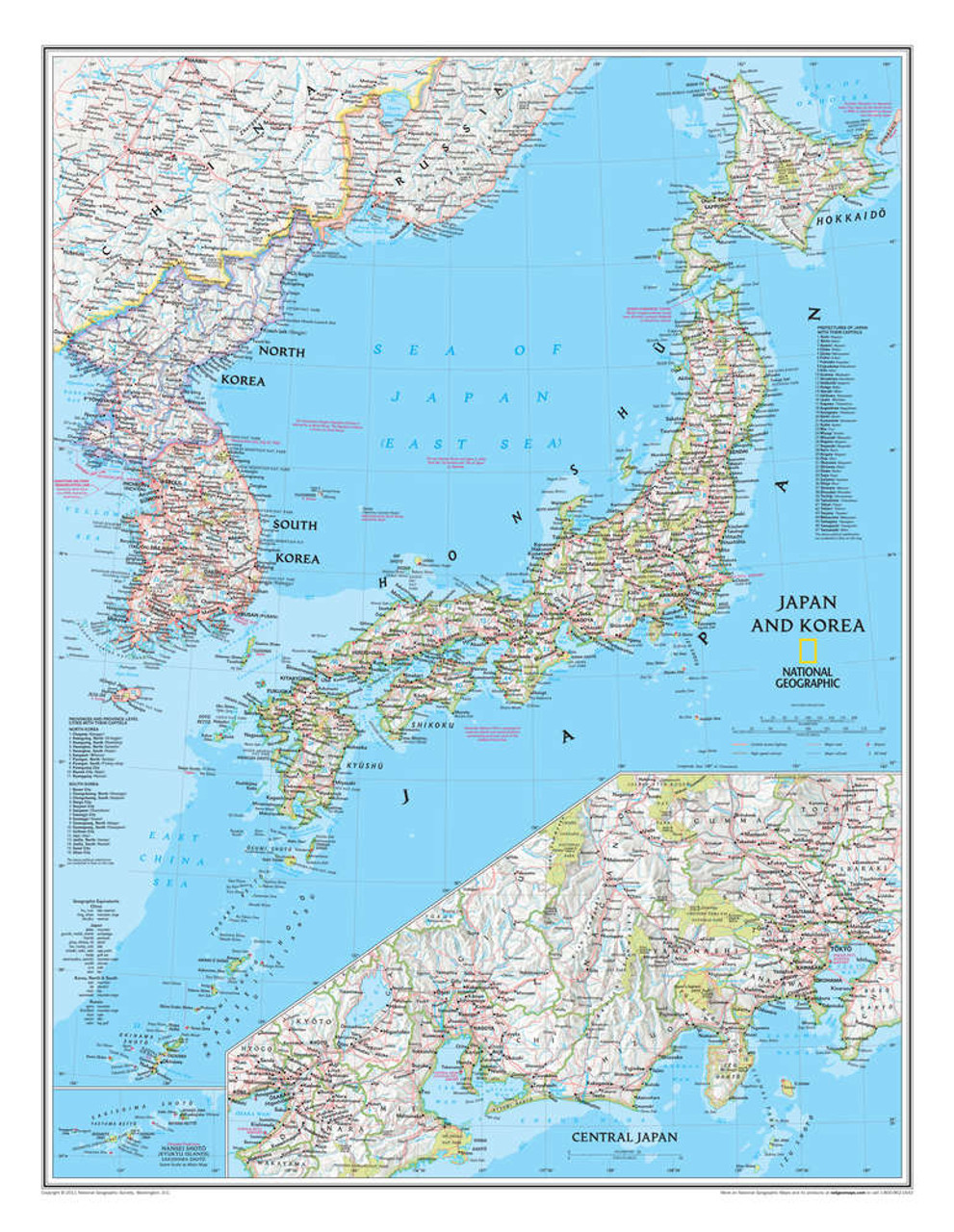
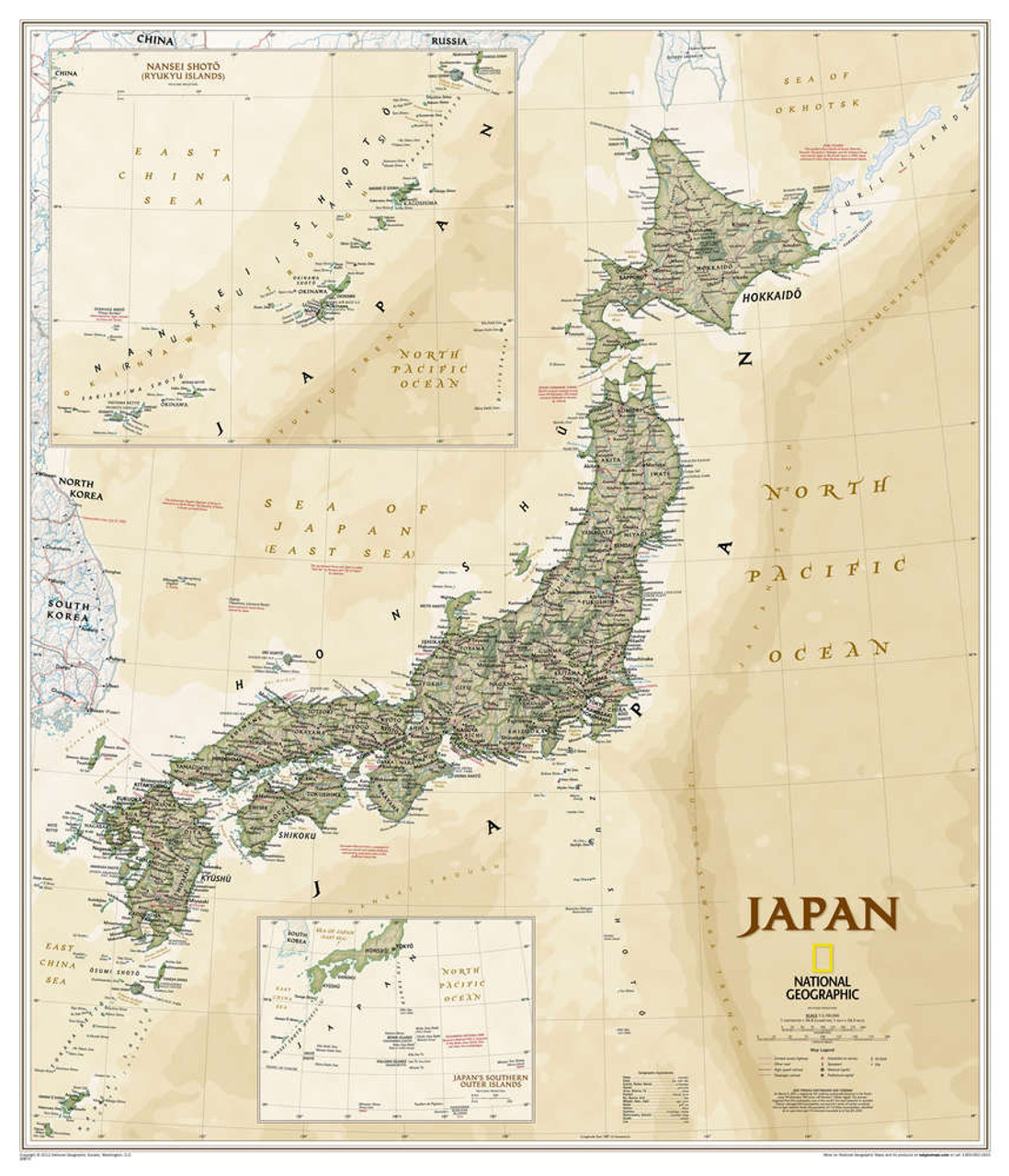
BAB 3: Mapping Japan: A Geographical Overview
Japan is a country known for its diverse and beautiful landscapes. From the snowy peaks of Hokkaido to the tropical beaches of Okinawa, Japan's topography is as varied as it is stunning. In this section, we will delve into the geographical aspects of Japan, exploring its regions and the unique features that make up its diverse landscape.
Sub Bab: Regions and Topography of Japan Japan is divided into eight regions, each with its own distinct characteristics. Hokkaido, located in the northern part of the country, is known for its cold winters and beautiful natural scenery. Tohoku, just south of Hokkaido, is famous for its hot springs and picturesque mountains. The Kanto region, home to Tokyo, is a bustling metropolis surrounded by rolling hills and coastline. Chubu, located in the central part of the country, is where the Japanese Alps are located, offering breathtaking views and skiing opportunities in the winter. Kansai, home to cities like Kyoto and Osaka, is known for its historical landmarks and cultural significance. Chugoku, located on the western end of Honshu, is known for its beautiful coastline and historical sites. Shikoku, an island to the south of Honshu, is famous for its natural beauty and the 88 Temple Pilgrimage. Finally, Kyushu, the southernmost of Japan's main islands, is known for its volcanic landscapes and hot springs.
Each region offers a unique perspective on Japanese culture and provides a glimpse into the country's rich history and traditions. The topography of Japan is equally diverse, with mountains, volcanoes, forests, and islands all contributing to the country's natural beauty. From the iconic Mount Fuji to the stunning beaches of Okinawa, Japan's topography is a testament to the country's natural wealth.
Japan's diverse topography has not only shaped the country's culture and traditions but has also influenced its art, literature, and way of life. Understanding the geographical overview of Japan is essential in gaining a deeper appreciation of the country's cultural wealth and diversity.
In conclusion, Japan's regions and topography offer a rich tapestry of landscapes and natural features that have played a significant role in shaping the country's cultural identity. By exploring the geographical diversity of Japan, we can gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of the cultural wealth that the country has to offer.
Chapter 4: The Cultural Wealth of Japan's Prefectures
In this chapter, we will delve into the cultural significance of Japan's prefectures and explore the historical background of each region. Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, each with its own distinct cultural identity and traditions. These prefectures play a crucial role in shaping the cultural wealth of Japan and provide a deep insight into the diverse heritage of the country.
Prefectures are administrative divisions in Japan, similar to states or provinces in other countries. However, they are not just administrative units; they also hold great cultural and historical significance. Each prefecture has its own unique customs, dialects, festivals, cuisine, and traditional arts, making them integral to the rich tapestry of Japanese culture.
Let's start by looking at the cultural significance of different prefectures. Japan's prefectures are known for their unique cultural practices, historical landmarks, and traditional crafts. For example, Kyoto, the former imperial capital of Japan, is renowned for its historic temples, gardens, and traditional tea houses. It is also a hub for traditional Japanese arts such as tea ceremony, flower arranging, and traditional dance. On the other hand, Okinawa, the southernmost prefecture of Japan, has a distinct Ryukyuan culture, with its own language, music, and traditional performing arts.
Understanding the historical background of each prefecture is essential to comprehending the cultural wealth of Japan. Many of Japan's prefectures have a long and vibrant history, with each region boasting its own unique traditions and folklore. For instance, Aomori Prefecture in northern Japan is famous for its Nebuta Matsuri, a lively summer festival featuring large, illuminated floats depicting historical and mythical figures. The festival has been celebrated for over 300 years and is deeply rooted in the region's history and culture.
Exploring the cultural wealth of Japan's prefectures also involves uncovering the traditional crafts and industries that have been passed down through generations. For example, Kanazawa, located in Ishikawa Prefecture, is known for its intricate lacquerware, gold leaf production, and traditional Kaga-Yuzen silk dyeing. The preservation of these traditional crafts is vital in maintaining Japan's cultural heritage and contributes to the uniqueness of each prefecture.
In sum, this chapter aims to highlight the incredible diversity and richness of Japan's prefectures, delving into their cultural significance and historical backgrounds. By understanding the cultural wealth of each prefecture, we gain a deeper appreciation for Japan's heritage and the integral role that these regions play in shaping the country's cultural identity.
Chapter 5 of the outline focuses on the depiction of legends and myths on Japanese maps. Maps are not just a tool for navigation, but they also serve as a medium for storytelling and representation of cultural beliefs. In Japan, maps have long been used to represent not just the physical landscape, but also the spiritual and mythical aspects of the country. This section will delve deeper into the fascinating world of Japanese map legends and myths.
The first subtopic under Chapter 5 will explore the depiction of legends and myths on Japanese maps. Japanese culture is rich with folklore and mythology, and these stories often manifest themselves in the way the land is represented on maps. For example, the famous legend of the dragon princess, which is associated with the formation of certain landscapes, may be represented through the use of symbols or illustrations on maps. Understanding these legends and myths is crucial to truly grasping the cultural wealth embedded in Japanese cartography.
The influence of folklore on map symbolism will be the second subtopic addressed in this chapter. Japanese folklore and mythology have heavily influenced the way certain landmarks and geographical features are depicted on maps. For instance, mountains and rivers may be named after deities or legendary creatures, and these names carry deep cultural and spiritual significance. By examining the connection between folklore and map symbolism, we gain a deeper understanding of how the Japanese view and interact with their natural environment.
In order to provide a comprehensive exploration of this topic, it is important to analyze the iconography on Japanese maps in relation to legends and myths. This subtopic will delve into the unique symbols and icons used in Japanese cartography and their meaning and significance in the context of folklore and mythology. These symbols may include representations of mythical creatures, sacred sites, or supernatural phenomena, all of which play a crucial role in conveying the cultural and spiritual dimensions of Japanese landscapes.
The overarching aim of Chapter 5 is to shed light on how Japanese maps serve as more than just geographical representations. They are also repositories of cultural stories and beliefs, with legends and myths woven into their very fabric. By studying the depiction of these legends and myths on Japanese maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural wealth of the country and the intricate ways in which it is expressed through cartography. This section will offer a comprehensive and insightful look at a lesser-explored aspect of Japanese cultural heritage, allowing readers to truly grasp the nuanced relationship between maps, legends, and myths in the Japanese context.
Chapter 6: Iconography on Japanese Maps
In this chapter, we will delve into the unique symbols and icons used in Japanese cartography, as well as the meaning and significance behind these symbols. Maps serve as a visual representation of the world around us, and the use of symbols and icons adds depth and layers of meaning to these representations.
Subsection 6.1: Unique Symbols and Icons Japanese maps are rich with unique symbols and icons that are not commonly found in maps from other cultures. These symbols can represent a variety of things, from historical landmarks to natural features to cultural elements. One of the most commonly used symbols is the cherry blossom, which represents the transient and ephemeral nature of life in Japanese culture. The use of Mount Fuji as a symbol on maps is also prevalent, as it is considered a sacred and iconic symbol in Japanese society. Additionally, maps often include symbols representing shrines, temples, and other religious sites, showcasing the deep spiritual connection that the Japanese people have with their surroundings.
Subsection 6.2: Meaning and Significance The symbols and icons used in Japanese maps are deeply rooted in the country's history, folklore, and traditions, each with its own unique meaning and significance. For example, the use of the torii gate symbol on maps indicates the presence of a Shinto shrine, serving as a gateway between the human and spiritual realms. This symbol not only provides information about the location of the shrine but also carries with it a profound cultural and spiritual significance.
The use of color in Japanese maps also holds symbolic meaning. For instance, the use of red often represents shrines and temples, while green may be used to denote areas of natural beauty, such as parks or gardens. These color choices are not arbitrary; they are steeped in cultural meaning and serve to provide a deeper understanding of the landscape being depicted.
Subsection 6.3: Evolution and Adaptation The symbols and icons used in Japanese maps have evolved and adapted over time, reflecting changes in society, technology, and cultural values. With the advent of modern cartography, the use of symbols has become more standardized, allowing for easier interpretation by a global audience. However, traditional symbols and icons still hold significant cultural value and continue to be used alongside modern conventions.
In recent years, there has also been a movement to incorporate more inclusive and diverse symbols on Japanese maps, representing the country's changing social landscape. This includes the inclusion of symbols representing accessibility features, LGBTQ+ spaces, and other aspects of a more inclusive society.
Overall, the iconography on Japanese maps is a fascinating and integral aspect of the country's cultural wealth. The symbols and icons used not only serve a practical purpose in navigating the physical landscape but also provide a window into the rich tapestry of Japanese history, traditions, and values. As we continue to explore and understand these symbols, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and depth of Japanese culture.
Chapter 7: Exploring Japanese Heritage Sites Through Maps
In this chapter, we will delve into the significance of mapping out heritage sites in Japan and how it plays a crucial role in preserving the country's cultural wealth. We will also explore how cartography can be used to promote and protect these important cultural sites for future generations.
Mapping Heritage Sites: Highlighting the Importance
Japan is home to a rich tapestry of heritage sites, including ancient temples, historical castles, traditional gardens, and UNESCO World Heritage sites. These sites not only represent Japan's cultural and historical significance but also serve as important tourist attractions. By mapping out these heritage sites, we can create a visual representation of Japan's cultural wealth, making it easier for people to navigate and appreciate the country's historical and artistic treasures.
Preserving Cultural Heritage through Cartography
One of the main benefits of mapping heritage sites is the preservation of cultural heritage. By documenting these sites on maps, we can ensure that they are accurately recorded and protected for future generations. This is particularly important in a country like Japan, where natural disasters and urbanization pose threats to historical landmarks. By creating detailed maps of these sites, we can better understand their geographical context and significance, leading to more effective preservation efforts.
Mapping out heritage sites also allows for easier access for researchers, historians, and tourists. It provides a comprehensive overview of the locations, significance, and historical background of each site, making it easier for people to plan and undertake cultural and historical tours. Additionally, it helps to raise awareness of these sites, attracting more visitors and contributing to the local economy.
Highlighting Heritage Sites on Maps
When it comes to mapping out heritage sites, it is important to provide detailed information about each location. This includes not only the geographical coordinates and physical features but also the historical and cultural context. By incorporating this information into maps, we can create a comprehensive guide to Japan's cultural wealth, allowing people to gain a deeper understanding of the significance of these sites.
Furthermore, the use of modern technology, such as interactive maps and virtual tours, can enhance the experience of exploring heritage sites. By incorporating multimedia elements into maps, we can provide more immersive and engaging experiences for users, further promoting the appreciation and preservation of Japan's cultural heritage.
In conclusion, mapping out heritage sites in Japan is essential for preserving and promoting the country's cultural wealth. By creating detailed and informative maps, we can ensure that these important sites are accurately recorded and protected for future generations. Additionally, mapping heritage sites enhances the accessibility and understanding of Japan's cultural and historical significance, contributing to the appreciation and preservation of these valuable assets. As technology continues to advance, there is a great potential for further exploration and representation of Japan's cultural diversity through cartography.
BAB 8: Menavigasi Kuliner Jepang Melalui Peta
Peta bukan hanya alat navigasi untuk menemukan lokasi geografis, tetapi juga dapat digunakan untuk menjelajahi kekayaan budaya suatu tempat, termasuk kekayaan kuliner. Jepang dikenal dengan keanekaragaman kuliner yang kaya dan beragam di setiap wilayahnya. Pada bagian ini, kita akan mengeksplorasi bagaimana peta dapat digunakan untuk memetakan kekayaan kuliner Jepang dan mewakili keanekaragaman kuliner tersebut.
Sub Bab 1: Spesialisasi Kuliner Regional yang Tercatat pada Peta Jepang memiliki banyak spesialisasi kuliner regional yang unik dan berbeda di setiap prefektur. Misalnya, Hokkaido terkenal dengan produk susu dan makanan lautnya, sementara Osaka dikenal dengan okonomiyaki dan takoyaki-nya. Dengan menggunakan peta, spesialisasi kuliner dari setiap wilayah dapat direpresentasikan dengan jelas. Peta dapat menunjukkan lokasi dan jenis makanan spesifik yang terkenal di setiap wilayah, sehingga pengunjung dapat dengan mudah menemukan dan menikmati makanan khas tersebut saat mengunjungi wilayah tersebut.
Sub Bab 2: Diversitas Kuliner yang Direpresentasikan pada Peta Tidak hanya spesialisasi kuliner regional, peta juga dapat digunakan untuk merepresentasikan keanekaragaman kuliner secara keseluruhan di Jepang. Dari hidangan klasik seperti sushi, ramen, dan tempura hingga hidangan lokal yang kurang dikenal, peta dapat menggambarkan berbagai jenis makanan yang dapat ditemukan di berbagai wilayah di Jepang. Dengan memetakan diversitas kuliner ini, peta dapat menjadi sumber informasi yang berharga bagi wisatawan yang ingin menjelajahi ragam masakan Jepang.
Dengan demikian, dapat disimpulkan bahwa peta bukan hanya alat navigasi, tetapi juga merupakan representasi visual yang kuat dari kekayaan kuliner suatu tempat. Melalui peta, keanekaragaman kuliner Jepang dapat dengan mudah diakses dan dipahami oleh masyarakat lokal maupun wisatawan. Selain itu, peta juga dapat menjadi alat promosi yang efektif untuk memperkenalkan kekayaan kuliner Jepang kepada dunia. Dengan menggunakan peta untuk menavigasi kekayaan kuliner Jepang, kita dapat mengeksplorasi dan memahami lebih dalam tentang kekayaan budaya yang dimiliki oleh negeri Sakura ini.
Chapter 9: Cultural Events and Festivals on Japanese Maps
Cultural events and festivals play a significant role in Japanese society, and they are deeply rooted in the country's rich cultural heritage. These events are celebrated throughout the year, and they are a reflection of the traditions, beliefs, and values of the Japanese people. In this chapter, we will explore how these cultural events and festivals are represented on maps, and the impact they have on promoting Japanese cultural wealth.
Subsection 9.1: Mapping out traditional festivals and events Traditional festivals, known as "matsuri" in Japanese, are an integral part of the country's cultural landscape. These festivals are held to honor and show gratitude to the Shinto deities, as well as to celebrate the changing seasons, the harvest, and various historical events. Each festival is unique to the region and often reflects the local customs and traditions. By mapping out these festivals, we can gain a better understanding of the diverse cultural practices and the significance of these events in different parts of Japan.
Using maps to showcase the locations of these festivals allows us to visualize the distribution and the frequency of these events throughout the country. It also helps to identify the specific customs and rituals associated with each festival, showcasing the diversity of Japan's cultural heritage. Additionally, mapping out these festivals can aid in promoting tourism and cultural exchange, as it provides a comprehensive overview of the various cultural experiences that can be enjoyed in different regions of Japan.
Subsection 9.2: Representation of cultural celebrations on maps In addition to traditional festivals, Japan also celebrates various cultural events that are of historical and contemporary significance. These events can range from religious ceremonies and processions to modern cultural celebrations, such as music festivals and dance performances. Mapping out these cultural celebrations provides a visual representation of the dynamic and vibrant cultural landscape of Japan.
By including these cultural celebrations on maps, we can highlight the diversity of cultural activities that take place throughout the country. This not only promotes awareness of these events but also encourages participation and engagement with Japanese culture. Furthermore, the representation of these cultural celebrations on maps serves as a powerful tool in preserving and promoting intangible cultural heritage, as it allows for the documentation and dissemination of these traditions to a wider audience.
In conclusion, mapping out traditional festivals and cultural celebrations in Japan not only serves to promote cultural awareness and exchange but also plays a crucial role in the preservation and promotion of Japan's rich cultural heritage. Through the visual representation of these events on maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and richness of Japanese culture. Additionally, the use of maps as a tool for promoting cultural events and festivals holds great potential for enhancing cultural tourism and fostering cross-cultural understanding. As we look towards the future, there is immense opportunity for further exploration and representation of Japan's cultural diversity through maps and legends.
Chapter 10: Future Prospects: Using Map and Legend to Share Japanese Culture
The final chapter of the outline focuses on the future prospects of using maps and legends to share Japanese culture. It emphasizes the potential for further exploration and representation of cultural diversity in Japan through cartography.
Subsection 1: Utilizing maps to promote Japanese cultural wealth
In this subsection, the focus is on the integration of modern technology and mapping tools to promote Japanese cultural wealth. With the advancement of digital mapping platforms and geographical information systems (GIS), there is an opportunity to create interactive maps that showcase the rich cultural heritage of Japan. These maps could be made accessible to a global audience, allowing people from around the world to explore and learn about the diversity of Japanese culture.
Furthermore, social media and online platforms can be utilized as channels for disseminating these cultural maps. By sharing them on various digital platforms, the reach of these cultural representations can be expanded, leading to a greater appreciation and understanding of Japanese cultural wealth.
Subsection 2: Potential for further exploration and representation of cultural diversity
This subsection delves into the potential for further exploration and representation of cultural diversity in Japan through cartography. It emphasizes the need for ongoing research and documentation of cultural practices, traditions, and historical sites that may not have been adequately represented in existing maps.
One avenue for achieving this is through collaborative projects involving local communities, scholars, and cartographers. By engaging with these stakeholders, it is possible to gather valuable insights and information that can be integrated into future maps. This collaborative approach not only ensures the accuracy and authenticity of the cultural representations but also fosters a sense of ownership and pride within the local communities.
Additionally, there is an opportunity to innovate and develop new mapping techniques that capture the intangible aspects of cultural diversity, such as language, music, and performing arts. By incorporating multimedia elements into maps, cultural richness can be conveyed in a more immersive and engaging manner, thus deepening the audience's understanding and connection to Japanese cultural wealth.
In conclusion, Chapter 10 highlights the immense potential for utilizing maps and legends to share Japanese culture with the world. By harnessing the power of technology, fostering collaboration, and embracing innovative mapping approaches, there is a bright future for representing and celebrating the cultural diversity of Japan through cartography. As we look ahead, it is crucial to continue nurturing this field of study and exploration, ensuring that Japanese cultural wealth is preserved and appreciated for generations to come.